
10) of the DICOM Standard gives the Transfer Syntax as a set of encoding rules that allow Application Entities to unambiguously negotiate the encoding techniques (e.g., Data Element structure, byte ordering, compression) they are able to support, thereby allowing these Application Entities to communicate. A Transfer Syntax tells how the transferred data and messages are encoded. Each device comes with its own DICOM Conformance Statement, which lists all transfer syntaxes acceptable to the device. In simple terms, it tells whether a device can accept the data sent by another device. One more important concept is Transfer Syntax. Similar is the case with other modalities. Repeat this for all entries in Table A.26-1. For example, from that table, again refer to C.7.1.1 to get the details corresponding to Patient. If your application deals with, for instance, Digital X-Ray, then, refer to Part 3 of the Standard (2011 version), Table A.26-1 to identify the mandatory and non-mandatory tags for this. 7.4 of Part 5 of the Standard (2011 version) gives the Data Element Type, where five categories are defined - Type 1, Type 1C, Type 2, Type 2C, and Type 3. The DICOM Data Dictionary gives a list of all the standardized Group and Element Tags.Īlso important is to know whether a tag is mandatory or not. In this example, 0010 (hex) is the Group Tag, and 0020 (hex) is the Element Tag. For example, the tag 0010 0020 (in hexadecimal) represents Patient ID, with a VR of LO (Long String). A tag is divided into two parts, the Group Tag and the Element Tag, each of which is of length 2 bytes. A tag is a 4 byte value which uniquely identifies that attribute. An important characteristic of VR is its length, which should always be even.Ĭharacterizing an attribute are its tag, VR, VM (Value Multiplicity), and value. Detailed explanations of these VRs are given in Part 5 (Sec. For example, DT represents Date Time, a concatenated date-time character string in the format YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.FFFFFF&ZZXX. There are 27 such VRs defined, and these are AE, AS, AT, CS, DA, DS, DT, FL, FD, IS, LO, LT, OB, OF, OW, PN, SH, SL, SQ, SS, ST, TM, UI, UL, UN, US, and UT. This 'data type' is termed as Value Representation (VR) in DICOM. As can be seen, these attributes require different data types for correct representation. An application which does not find a needed attribute name in this standardized list may add its own private entry, termed as a private tag proprietary attributes are therefore possible in DICOM.Įxamples of attributes are Study Date, Patient Name, Modality, Transfer Syntax UID, etc. DICOM has also standardized on the most commonly used attributes, and these are listed in the DICOM Data Dictionary (Part 6 of the Standard).
In other words, an IOD is a data abstraction of a class of similar real-world objects which defines the nature and attributes relevant to that class. An IOD is a collection of attributes describing a data object. DICOM objects are standardized according to IODs ( Information Object Definitions). An object, as in Object Oriented Programming, is characterized by attributes. In particular, we do not discuss the communication and network aspects of the DICOM standard.Įverything in DICOM is an object - medical device, patient, etc. In what follows, we explain only those terms and concepts related to a DICOM file. All of these details are hidden inside the DICOM file in the form of tags and their values.īefore we get into tags and values, a brief about DICOM itself and related terminology is in place. Important among the image details are the image dimensions - width and height, and image bits per pixel. The header comprises, among other things, the patient name and other patient particulars, and image details. As with all other image file formats, a DICOM file consists of a header, followed by pixel data. We now present a brief description of the DICOM image file format.

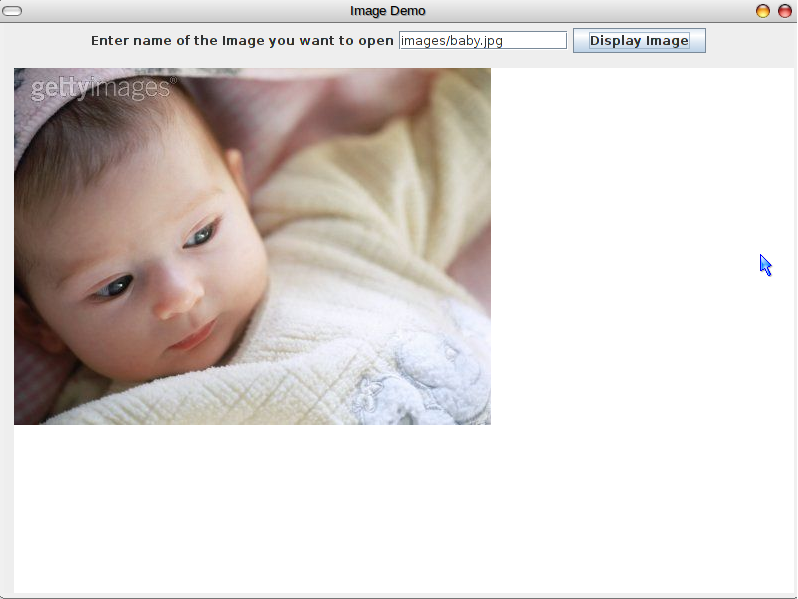
We also demonstrate the way to modify the brightness and contrast of the displayed image through Window Level. In this article, we present a viewer for DICOM images. Within the innards of the standard is also contained a detailed specification of the file format for images. The standard comprises of twenty parts (as of 2013), and is freely available at the NEMA website. The DICOM standard was created by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), and it also addresses distribution and viewing of medical images. The DICOM standard addresses the basic connectivity between different imaging devices, and also the workflow in a medical imaging department.
Image viewer project in java with source code download#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
